Cost of Turned Parts
With advancements in science and technology, significant changes have occurred in turning machinery and components. From traditional manual lathes (referred to as “conventional lathes”) to automatic lathes with cam mechanisms (“automatic lathes”) and computer numerical control lathes (“CNC lathes” or “computer lathes”), these innovations have greatly improved the overall machining accuracy, speed, and product consistency of processed parts. Different types of turning equipment lead to varying costs for the same part, resulting in different pricing. Therefore, selecting the right machining method is crucial, requiring engineers estimating part prices to have a deep understanding of machining processes and equipment. Reasonable manufacturing costs also rely on strict quality control standards.
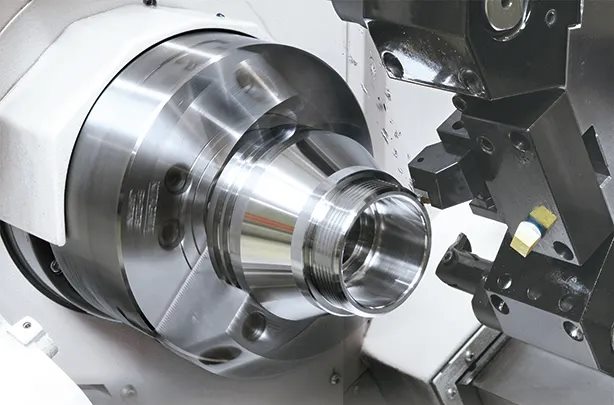

Regardless of the lathe used, the price of turned parts can be calculated using the formula:
Material Cost + Machining Cost + Post-Processing Cost (heat treatment, surface treatment, etc.) + Packaging Cost.
Material Cost for Turning
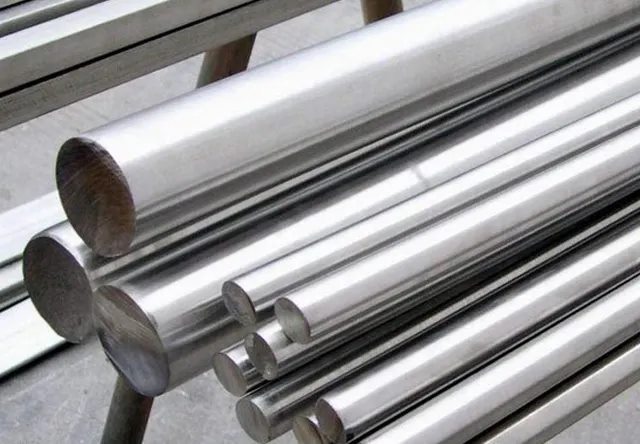
The first component is material cost, which is straightforward to calculate. Determine the volume of material required for the part, multiply it by the material’s density (density varies by material and can be found online) to obtain the weight of the raw material. Then, use the formula:
(Part Weight × Material Unit Price = Part Material Cost).
This cost tends to be consistent across companies, with minimal variation in valuation.

Machining Cost for Turning
The second component is machining cost, which relies on the expertise of evaluation engineers. The largest difference in product valuation between enterprises lies in machining costs. Engineers must analyze the part’s design drawings, machining processes, technical requirements, and the advantages of different lathes. Since machining precision and efficiency vary by lathe type, the same operation can have different costs on different machines. Below is an overview of cost estimation for lathe machining and processes:
Key Factors Influencing Machining Costs:
- Lathe Type:
- Conventional Lathes: Cost-effective for small batches (e.g., single pieces or low-volume production) of parts without complex rotational surfaces.
- Automatic Lathes: Offer price advantages for high-volume production of small-diameter parts with low-precision requirements due to high efficiency.
- CNC Lathes: Necessary for large-scale production of high-precision, large-dimension parts. In competitive markets, selecting the right lathe gives a pricing edge.
- Process Optimization:
- Requires skilled programmers and rational process planning for different materials, including optimal tool paths, minimized idle movements, suitable cutting tools, and balanced machining speeds/feed rates. These factors enhance efficiency and ensure quality, making skilled machinists critical to competitive pricing.
- Time-Based Costing:
- Machining costs are typically calculated by time, with rates ranging from ¥45–60 per hour in most companies. For example, machining a CNC part with a 0.5-minute clamping time and 4-minute machining time at a ¥1 per minute rate (¥60/hour) would cost ¥4.50.
Post-Processing Cost for Parts
The third component is post-processing cost, including:
- Heat Treatment Costs
- Surface Treatment Costs (electroplating, electrophoresis, anodizing, powder coating, painting, QPQ, etc.)
- Logo Printing
This cost depends on customer requirements; some projects may omit it. Industry benchmarks for pricing include: - Heat treatment: Usually priced by weight.
- Surface treatment: Priced by weight or surface area, with the higher of the two rates typically applied.
Comprehensive Cost Calculation
While the basic formula includes material, machining, and post-processing costs, some companies add management fees and profit margins, especially in complex 报价 (quotations) for large enterprises. Simplified estimates often incorporate these into machining costs.

Debaolong Seiko—Your Precision CNC Partner
As a leading CNC expert in China, Debaolong Seiko helps clients save 30% costs while delivering high-quality parts. Why not experience our precision and efficiency today?
Contact us to optimize your turning projects: www.debaoloong.com