Aluminum (Al) is a versatile element renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and excellent electrical conductivity. However, a key property influencing its processing techniques and applications is its melting point—the temperature at which the metal transitions from a solid to a liquid phase. Engineers and metallurgists consistently recognize it as a critical factor in any industrial process involving high-temperature applications. This article discusses the significance of aluminum’s melting point and its impact on various characteristics.
What is the Melting Point of Aluminum?
The melting point is the temperature at which any solid transitions to a liquid state. For 99.99% pure aluminum, the melting point is 660.37°C. Slight variations occur with different purity levels:
- 99.5% aluminum: 657°C
- 99.0% aluminum: 643°C
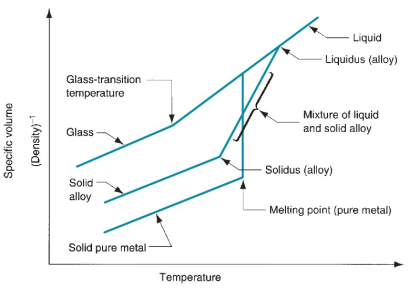
Understanding the Melting Point
Aluminum Melting Point in Kelvin
Aluminum’s melting point in Kelvin is 933.5K.
Why is the Melting Point Important?
The melting point is critical for industrial and high-temperature applications, such as determining aluminum casting or welding temperatures. Inadequate or incorrect melting temperatures can lead to structural defects, poor production performance, and errors in heat treatment, welding, or other processes—ultimately increasing costs.

Volume Changes in Pure Metals (Crystalline Structures) vs. Glass (Amorphous Structures)
Boiling Point of Aluminum
Aluminum’s boiling point is 2,470°C. A higher boiling point indicates tighter ion packing and stronger bond strength, requiring more energy to vaporize.
Melting Points of Common Aluminum Grades
Different aluminum alloys have melting temperatures distinct from pure aluminum due to variations in composition, structure, and alloying elements:
- 6061 aluminum alloy: 580–650°C
- 6061 T6 aluminum: 582–635°C
- 7075 aluminum: 475–635°C
- 2024 aluminum: 500–635°C
Melting Temperature of Aluminum Oxide
Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) has a significantly higher melting point of 2,072°C. This is due to its ionic bonding (with some covalent character), which requires more energy to break than the metallic bonds in pure aluminum.
Relationship Between Aluminum’s Melting Point and Other Physical Properties
Physical properties like thermal capacity, thermal conductivity, and thermal expansion are directly linked to melting temperature and influence how aluminum behaves at different temperatures. Aluminum exhibits ductile fracture behavior across all temperatures, but low-temperature conditions can alter its toughness, durability, ductility, and strength.
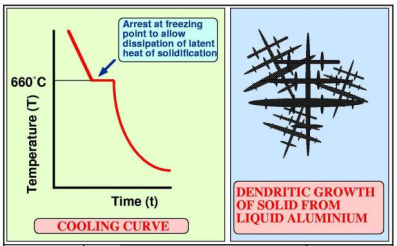
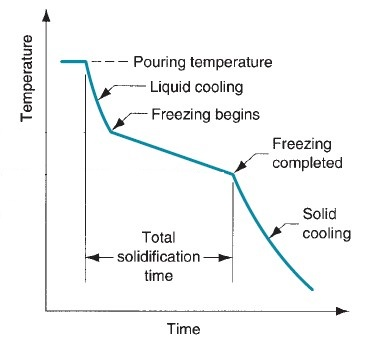
Solidification of Aluminum
Factors Influencing Aluminum’s Melting Point
Purity and Alloying Elements
- Purity: Higher impurity levels (e.g., silicon, iron) lower the melting point while enhancing mechanical properties like tensile and compressive strength.
- Alloying Elements: Additions of copper, silicon, or iron reduce the melting point but affect phase stability and structural integrity.
Role of Impurities in Lowering Melting Point
Impurities introduced during extraction or processing (e.g., copper, silicon) disrupt the pure aluminum lattice, reducing the energy required for melting.
Microstructural Impact on Melting Behavior
- Grain Size: Smaller grain sizes in the microstructure lower the melting point and reduce latent heat of fusion.
- Coatings: Surface coatings on aluminum components can increase the melting point.
Pressure
- Higher pressure generally raises the melting point, as more energy is required to overcome interatomic forces. An exception is ice/water, where pressure lowers the melting point.
Heating Rate
- Slow Heating: Allows gradual structural changes, enabling precise melting point determination.
- Rapid Heating: Can cause “melting point hysteresis,” where the measured melting point is higher due to delayed structural adaptation.
Applications of Aluminum’s Melting Point
Aluminum Casting
- Temperature Control: Casting temperatures must be moderate. Too low a temperature causes poor fluidity and defects like shrinkage; too high leads to thermal cracking and porosity in the final component.
Aluminum Welding
- Welding Temperature: Inadequate heat causes cold cracking, while improper thermal management leads to insufficient fusion between the weld metal and base material.
- ** Fusion Welding**: Incorrect temperatures result in lack of penetration and weld cracks.
- Solid-State Welding: Extreme temperatures weaken the weld; low heat causes shallow penetration and weak joints.
Measuring and Controlling Aluminum’s Melting Point
Temperature Measurement Tools
- Thermocouples: Sensors using two dissimilar metal wires to measure temperature via electrical signals.
- Pyrometers: Non-contact devices measuring high temperatures by detecting thermal radiation, ideal for furnaces.
Melting Point Determination Methods
- Capillary Method: Traditional technique using a capillary tube to observe phase change.
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC): Measures heat flow and temperature changes to analyze physical properties.
- Hot Stage Microscopy: Combines microscopy with thermal analysis to study material behavior during heating.
Comparison of Aluminum’s Melting Point with Other Metals
| Metal | Melting Point (°C) | Comparison with Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 660°C | Lower than steel, copper, iron, and brass |
| Steel | 1370°C | Higher than aluminum |
| Copper | 1084°C | Higher than aluminum |
| Iron | 1510°C | Higher than aluminum |
| Brass | 930°C | Higher than aluminum |
FAQs
- What is the easiest metal to melt?
- Mercury, with the lowest melting point at -39°C.
- Can a gas stove melt aluminum?
- No, gas stoves typically do not reach the ~660°C required to melt aluminum.
- Which metal has the highest melting point?
- Tungsten, with a melting point of 3,399°C
For a detailed understanding of how we can assist with your projects, please visit www.debaoloong.com and collaborate with Debaolong Seiko.