Between a car’s engine block and cylinder head lies a cylinder head gasket. This small component seals the internal combustion process and facilitates the flow of oil and coolant within the engine. A blown gasket can cause severe engine issues. This article covers how gaskets fail, symptoms to identify, and corrective measures to prevent damage.
What is a Cylinder Head Gasket?
Cylinder head gaskets are typically made of multi-layered steel with elastomers, ensuring durability and a long service life. They seal the cooling and lubrication systems, enable the engine to generate sufficient power for propulsion, and allow harmful gases to exit through the exhaust system. As a critical part of internal combustion engines, they maintain pressure in the combustion chamber (where pistons operate) during ignition.
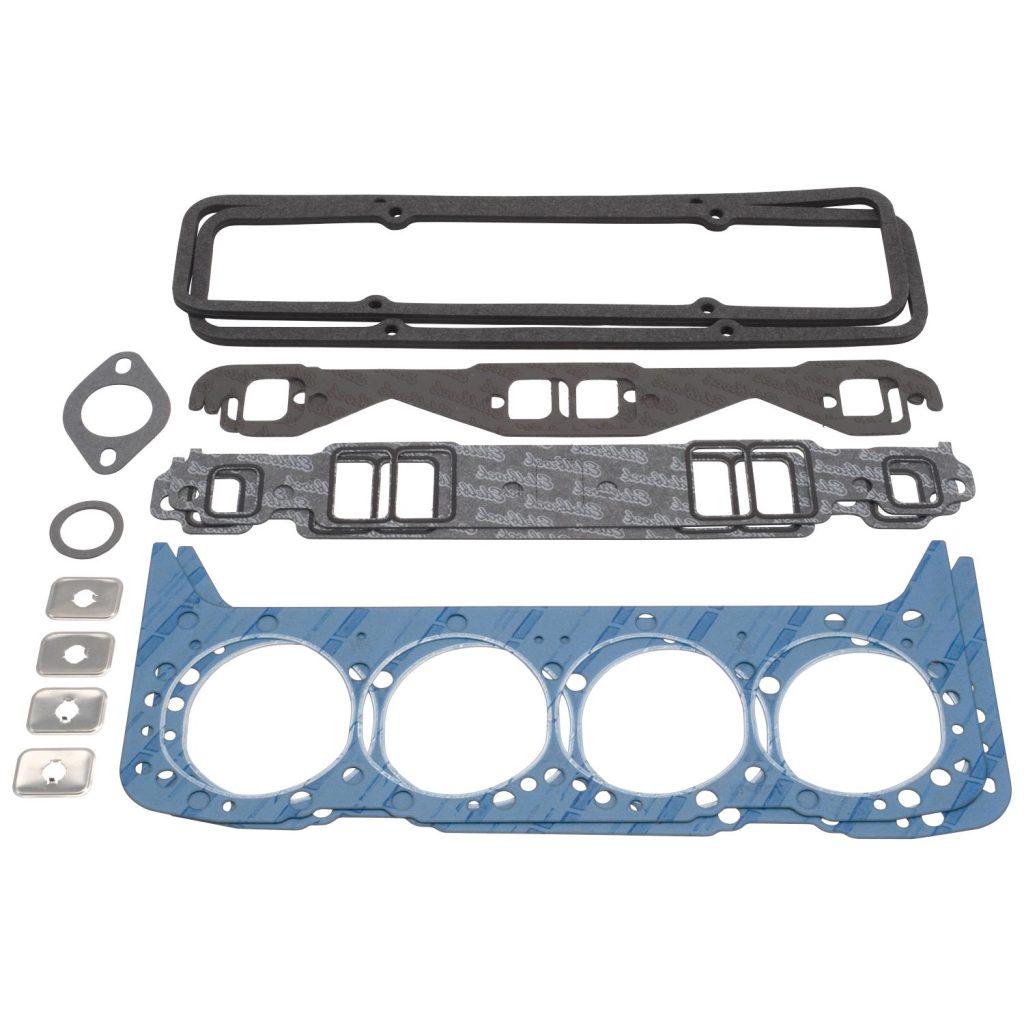

Where is the Cylinder Head Gasket Located?
It sits between the cylinder head (top of the internal combustion engine) and the engine block, withstanding extreme temperatures and pressures.
Cost to Replace a Cylinder Head Gasket
Replacement costs can be high, reaching up to $1,500, as it is a labor-intensive task. Hiring a professional mechanic or qualified technician is crucial for proper replacement.
Can You Drive with a Damaged Cylinder Head Gasket?
No, it is strongly advised against. A damaged gasket can cause severe issues like overheating, power loss, burns, or even fires.
What Role Does a Cylinder Head Gasket Play in a Car?
The cylinder head gasket is essential for engine operation, serving multiple functions:
- Sealing the Combustion Chamber
It maintains engine pressure, preserves power, and seals the internal combustion chamber. This ensures the compression from fuel vapor ignition (by spark plugs) remains within the chamber. - Lubrication and Cooling Systems
It allows oil and coolant to flow through the engine while keeping them separate to prevent fuel contamination. - Preventing Leaks
It stops coolant and oil from leaking, which could cause overheating and fires.
How Does a Cylinder Head Gasket Work?
- Sealing Between Engine Block and Cylinder Head
The cylinder head sits atop the engine, with the gasket sandwiched between the block and head. It retains pressure in the combustion chamber, generated by spark plug-ignited fuel vapor. - Regulating Pressure and Temperature
The gasket controls engine operation, enabling sufficient power for propulsion. It withstands high pressures and temperatures from power generation and spark plug ignition. - Ensuring Proper Fluid Flow (Oil, Coolant)
It circulates coolant (water) and lubricating oil through the engine, preventing overheating. Thus, it functions as part of both the cooling and lubrication systems.
What Causes a Cylinder Head Gasket to Blow?
Gasket failure can result from several factors:
- Engine Overheating
Excessive heat buildup can overwhelm the gasket, causing failure. It may also warp or crack the cylinder head or engine block, 破坏 the gasket’s sealing mechanism. - Poor Maintenance and Wear
Low engine oil, low coolant (without leaks), or premature spark plug ignition (due to wear) can damage the gasket over time. - Manufacturing Defects and Material Fatigue
Bubbles in the radiator or coolant tank, improper installation of new gaskets, or failure of the fire ring (sealing bead) can cause gasket blowouts.
Signs of a Damaged Cylinder Head Gasket
Watch for these indicators of a blown gasket:
- White Smoke from the Exhaust
A large volume of white smoke suggests coolant leaking into the cylinders, vaporizing during combustion. - Bubbles in the Coolant Reservoir
Gases entering the cooling system create bubbles, even when the engine is off. - Milky Oil (Coolant Contamination)
A gasket failure between cooling and lubrication channels mixes water with oil, creating a milky or foamy texture. - Engine Overheating
Overheating is a clear, common sign, often accompanied by steam or unusual odors. - Unexplained Coolant Loss
Leaks may indicate a gasket issue, though not all leaks stem from gasket failure.

How to Prevent Cylinder Head Gasket Damage
- Temporary vs. Permanent Solutions
There are no reliable temporary fixes. Regular oil/coolant changes and proper maintenance are essential. - Permanent Prevention Measures
- Ensure proper cylinder head installation.
- Use high-quality gaskets to avoid further damage.
- Use fuel with the correct octane rating.
- Maintain the cooling system and engine regularly.
- Monitor the temperature gauge consistently.
How to Customize a Cylinder Head Gasket
While standard gaskets are steel-based, custom versions can use materials like silicone, fiberglass, Teflon, or rubber.
How to Choose Cylinder Head Gasket Material
Material selection depends on: compatibility with operating conditions, working temperature, flexibility, surface finish, and corrosion resistance. Common materials include steel, copper, composites, and rubber.
CNC Machined Cylinder Head Gaskets
CNC machining produces gaskets with high dimensional precision and accuracy. It supports diverse materials, such as silicone, rubber, cork, felt, nitrile rubber, neoprene, glass fiber, polymers, and multi-layered steel with elastomers.
Stamped Cylinder Head Gaskets
This process uses progressive dies to stamp and assemble gaskets for automotive engine blocks. It performs tasks like stamping, bending, and forming, enabling efficient, safe production of complex shapes.
For more information, contact Debaolong Seiko. You are also welcome to upload your designs to Debaolong Seiko for a quote.