If you’ve ever watched a CNC machine in operation, you’ll know it’s loud, hot, and fast. Managing heat and friction in CNC machining is crucial for maintaining precision and tool life. Excess heat, generated primarily by friction between the cutting tool and the workpiece, can cause premature tool wear, poor surface finishes, and even material distortion.
This is where cutting fluids come in. Also known as metalworking fluids or machining coolants, these fluids serve multiple functions: they dissipate heat, reduce friction, and help remove chips from the cutting area. Choosing the right fluid can significantly improve machining efficiency, extend tool life, and enhance the overall quality of finished parts.
Read on to learn more about the role of cutting fluids in CNC machining, their types, and how to select the right one for optimal performance. This article also includes best practices for maintenance and proper disposal to ensure efficiency and compliance.
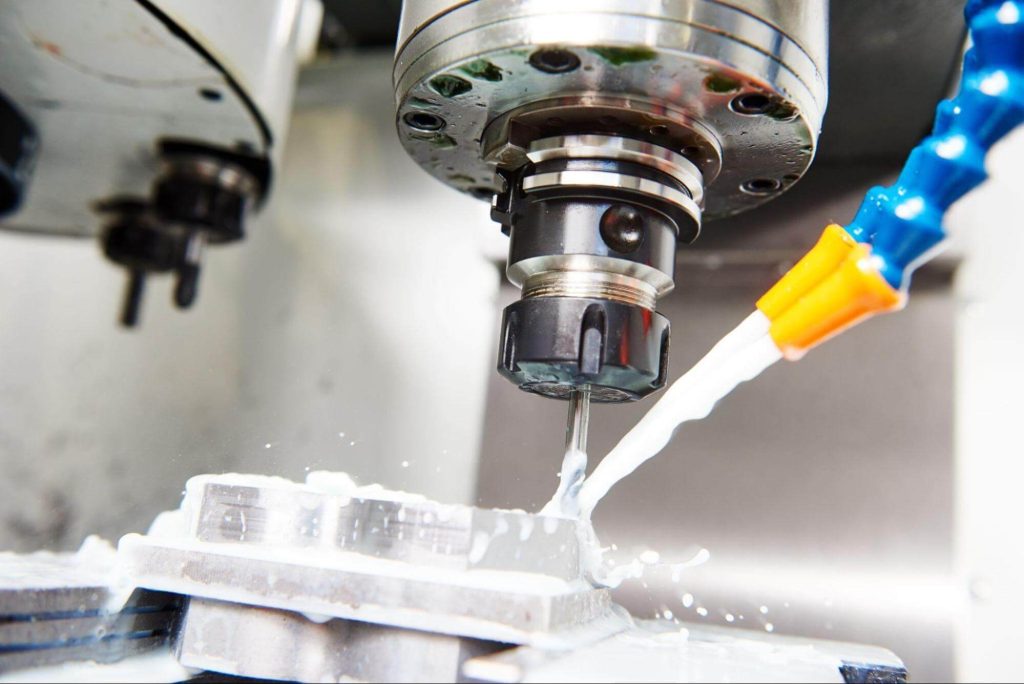

The Role of Cutting Fluids in CNC Machining
Cutting fluids play a vital role in ensuring smooth machining operations. In CNC machining, they are essential due to several key benefits:
- Cooling
- Lubrication
- Chip Removal
- Corrosion Protection
- Productivity Enhancement
Cooling
High cutting speeds in CNC machining generate significant heat, which can lead to rapid tool wear and potential workpiece deformation. Effective cooling is critical for maintaining machining accuracy and extending tool life. Water-soluble cutting fluids (such as emulsions, semi-synthetic, and synthetic fluids) play a key role in thermal management by absorbing and dissipating excess heat, preventing overheating of cutting tools and workpieces. This ensures smoother operations, longer tool lifespans, and improved machining efficiency.
Lubrication
Lubrication reduces friction between the cutting tool and the workpiece, minimizing tool wear and making the entire operation more efficient. Cutting fluids, such as neat oils (mineral, synthetic, or vegetable-based), provide much-needed lubrication to cutting tools, reducing friction between the tool and workpiece. This is key to reducing tool wear and improving the efficiency of the overall machining process.
Good lubrication helps reduce tool chatter and vibration, improves surface finish, and prevents material adhesion (built-up edge formation).
Chip Removal
Cutting fluids help clear metal chips from the cutting zone. This prevents the tool from recutting chips, which could damage both the tool and the workpiece. High-pressure coolant systems using synthetic fluids excel at flushing chips away, ensuring cleaner cuts and higher precision.
Cutting fluids also improve the quality of machined workpieces by constantly clearing metal swarf and chips from the tool and cutting area. This cleaning action helps prevent defects and ensures smoother surfaces.
Corrosion Protection
Some cutting fluids contain anti-corrosion additives that protect tools and workpieces from rust and oxidation. This is particularly important when machining materials like aluminum and steel. Adding corrosion inhibitors to cutting fluids reduces the risk of corrosion on machine parts and tools. These chemicals form a protective layer on metal surfaces, preventing damage from moisture and other corrosive agents.
Productivity Enhancement
Cutting fluids are crucial for boosting productivity in machine shops by enabling higher machining speeds and better surface finishes. By reducing tool wear and improving workpiece quality, they minimize downtime and optimize the overall efficiency of the production process.

Types of CNC Cutting Fluids
CNC machining cutting fluids are categorized into three main types based on their composition and primary functions:
- Neat Oils: Pure oil-based fluids that offer excellent lubrication but minimal cooling.
- Water-Soluble Fluids: Fluids mixed with water to enhance cooling efficiency.
- Chemical Cutting Fluids: Engineered fluids containing chemical additives to boost performance, often including synthetic and semi-synthetic formulations.
Within these types, cutting fluids are further divided into four main categories based on their formulation and applications:
- Water-soluble cutting fluids
- Synthetic cutting fluids
- Semi-synthetic fluids
- Neat oils
Water-Soluble Cutting Fluids
Water-soluble cutting fluids, including emulsions (soluble oils), semi-synthetics, and synthetics, are widely used in CNC machining due to their ability to balance cooling and lubrication. These fluids, which account for 80–90% of machining applications, are mixed with water to enhance heat dissipation and machining efficiency.
Emulsions combine oil and water, striking a good balance between cooling and lubrication. While water-soluble fluids are less lubricating than neat oils, they are ideal for high-speed machining and materials like aluminum and ferrous metals. However, they require regular monitoring to prevent bacterial growth and maintain performance.
Synthetic Cutting Fluids
Synthetic fluids are entirely chemical-based, containing no mineral oil, making them highly resistant to bacterial growth and degradation. They offer excellent cooling and minimal residue, making them ideal for high-speed CNC machining, grinding, and aerospace applications. However, they provide less lubrication than neat oils, which may be a consideration for specific machining processes.
Semi-Synthetic Fluids
Semi-synthetic fluids are a blend of synthetic oils and soluble oils, offering a balanced combination of lubrication, cooling, and cleanliness, making them ideal for versatile CNC machining. They do, however, require constant monitoring of concentration levels to maintain optimal performance.
Neat Oils
Neat oils are non-water-miscible lubricants that provide excellent friction reduction and tool protection. They often contain additives like sulfur, chlorine, or phosphorus to enhance cutting performance. Neat oils are generally divided into two types: standard neat oils and highly compounded neat oils.
Standard neat oils are 100% petroleum-based and offer excellent lubricity, creating a buffer effect between the workpiece and cutting tool. These oils are particularly effective in low-speed, high-precision machining operations requiring superior surface finishes. Despite higher costs, they are the preferred choice for demanding applications like broaching and deep-hole drilling due to their superior lubricating properties.
Highly compounded neat oils are specially formulated to enhance lubricity and are often used for machining difficult-to-cut metals like titanium, stainless steel, and high-temperature alloys. While neat oils excel in lubrication, their cooling properties are poor, and they may produce fumes or mist, which should be considered in the machining environment.
| Coolant Type | Composition | Most Common Applications | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soluble (Water-Based) | Oil-in-water emulsions; blend of oil-based or water-based fluids (mineral-based), surface-active additives (e.g., rust inhibitors, defoamers, pH stabilizers, emulsifiers), lubricants, corrosion agents, and detergents/dispersants. | Versatile and stable, with excellent cooling and lubrication. Suitable for cutting and grinding light to heavy metals, providing good surface finishes. | Multipurpose; used in lower-precision applications (e.g., hardware parts) and tighter-tolerance applications (e.g., bicycles, automotive, construction, aerospace). |
| Synthetic (Water-Based) | No petroleum-based oils; instead, a blend of rust inhibitors and water-soluble synthetic lubricants. Typically supplied as concentrates, requiring mixing with water to create usable coolant. | Designed for specific applications, offering superior cooling and lubrication compared to other water-based coolants. Preferred for high-speed cutting, hard material CNC machining, or achieving tight tolerances. | High demand in applications where precision and surface finish are critical, such as aerospace machining. |
| Semi-Synthetic (Water-Based) | Blend of engineered synthetic fluids (polyethylene glycols, polyalphaolefins), mineral oils, and surface-active additives (e.g., rust inhibitors, defoamers, pH stabilizers, emulsifiers, lubricants, detergents/dispersants). | Balances cost-effectiveness and performance; ideal for general CNC milling, turning, and drilling. | Metal fabrication, automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. |
| Neat (Straight) Oils | Offer optimal lubricity but minimal cooling; may contain organic lubricants (vegetable oils, fats, esters); biodegradable options available; sometimes blended with petroleum or mineral oils to enhance lubricity; may include chlorine, phosphorus, or sulfur additives. | Heavy-duty machining, high-speed processing, hard metal machining, thread cutting, tapping, screw machining, gear cutting. | Automotive, heavy machinery, metal fabrication, tool and die making, and precision engineering. |
How to Choose the Right Cutting Fluid for Your Application
Selecting the right cutting fluid requires careful evaluation of these key factors to optimize machining efficiency while minimizing costs and health risks:
- Cost and long-term value
- Material compatibility
- Fluid lifespan and maintenance
- Environmental regulations
Cost and Long-Term Value
Neat oils typically have a higher upfront cost than water-soluble fluids due to their composition and high-quality base oils. However, their superior lubricity and extended tool life can reduce overall expenses. A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is crucial to determine if the higher initial investment translates to long-term savings through reduced wear, improved machining quality, and extended fluid life.
Material Compatibility
Different materials require specific fluid properties. High-speed machining benefits from synthetics due to their superior cooling, while tough materials like steel and titanium require neat oils for enhanced lubrication and protection.
Fluid Lifespan and Maintenance
Beyond purchase price, consider fluid lifespan and maintenance. High-quality fluids may have a higher initial cost but often last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacement. While neat oils require less maintenance than water-soluble oils, they still need filtration and antioxidants to prevent oxidation and contamination, adding to operational costs.
Environmental Regulations
Proper disposal of cutting fluids is critical, as some may be classified as hazardous waste. Compliance with local disposal regulations impacts environmental responsibility and operational costs.
By considering all these factors, manufacturers can refine their machining processes while minimizing costs and health risks. Recommended metal cutting fluids based on key objectives are summarized below:
| Primary Objective | Recommended Cutting Fluid |
|---|---|
| High-speed machining | Synthetic or semi-synthetic |
| Heavy cutting (steel, titanium) | Neat oil or emulsion |
| Precision machining | Water-soluble fluid |
| Chip removal | High-pressure synthetic fluid |
| Environmental concerns | Vegetable oil |
Table: Recommended Metal Cutting Fluids
Always check the tool manufacturer’s recommendations for the best cutting fluid to use.
Cutting Fluid Maintenance and Disposal
Proper cutting fluid maintenance can extend tool life, prevent contamination, and reduce costs by ensuring optimal performance. Responsible disposal is equally important for environmental compliance, so following best practices for fluid management and waste reduction is critical.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Key practices for proper cutting fluid maintenance include:
- Monitoring concentration levels using a refractometer or chemical titration for accuracy.
- Maintaining pH levels between 8.5 and 9.5 to prevent bacterial growth and ensure fluid stability.
- Regularly removing tramp oil to maintain fluid performance and reduce disposal costs.
- Installing filtration systems to help eliminate metal fines and contaminants, extending fluid life.
- Providing proper training to ensure operators can identify fluid degradation and perform routine maintenance effectively.
Proper Disposal
To minimize environmental impact and avoid legal penalties, consider these practices to comply with environmental regulations:
- Establishing recycling programs to extend fluid life through filtration and reprocessing, reducing waste and costs.
- Following hazardous waste guidelines, which require testing before disposal to properly handle harmful chemicals.
- Using coolant management systems to help maintain fluid quality and minimize waste.
- Using biodegradable cutting fluids to reduce environmental impact; companies must adhere to disposal regulations to prevent fines and remediation costs.
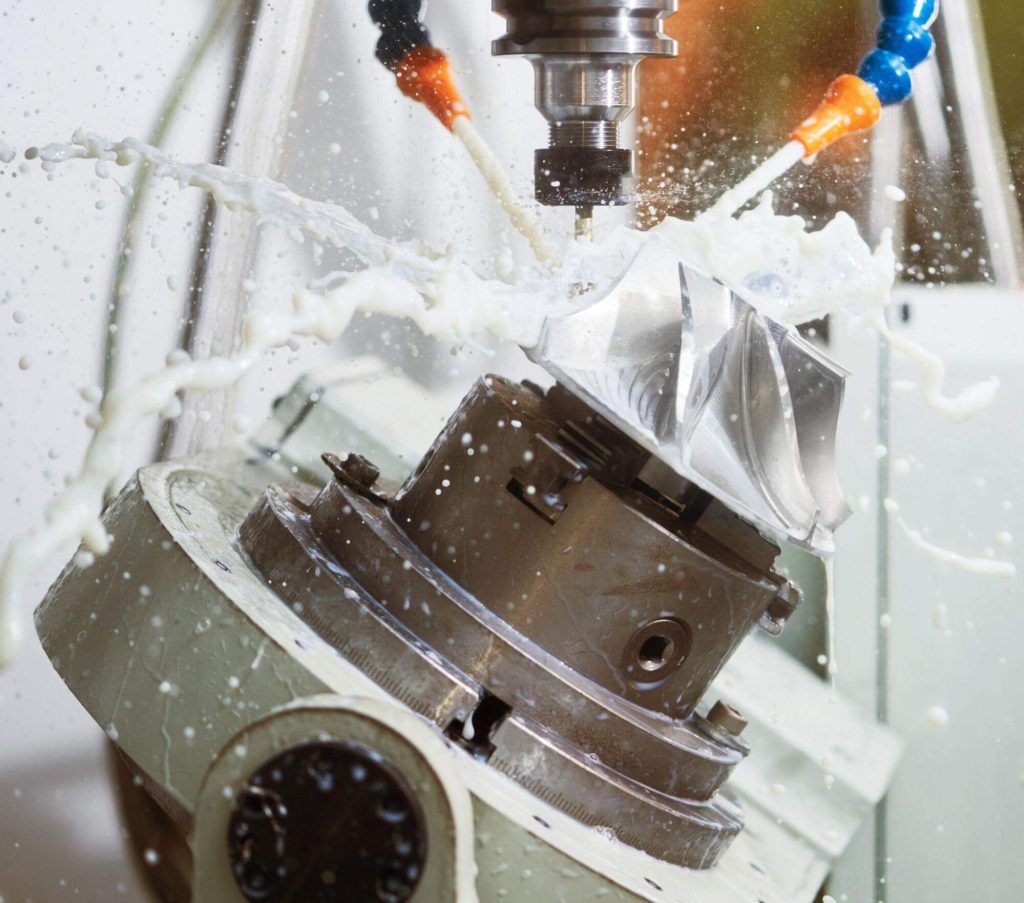

Future Trends in Cutting Fluids
As CNC machining continues to advance, innovations in metal cutting fluids aim to improve efficiency and help reduce environmental impact:
- Eco-Friendly Fluids: Vegetable oils and biodegradable coolants are growing in popularity. When used with minimum quantity lubrication (MQL), vegetable oils—especially coconut oil—actually outperform traditional options in terms of tool life and chip thickness.
- AI-Driven Fluid Monitoring: Sensors that detect contamination in real time use artificial intelligence to analyze and track fluid conditions. This optimizes performance, catches anomalies, and improves efficiency.
- Nano-Enhanced Lubricants: Cutting-edge fluids with superior cooling and wear resistance use nanoparticles to enhance thermal conductivity and lubrication.
- Reduced Cutting Fluid Use: There is a growing trend toward minimizing or eliminating cutting fluids in machining. Strategies like MQL and dry machining are being explored to reduce fluid consumption while still maintaining performance.
- Innovative Fluid Types: Development of new fluid formulations is expected to continue, with a focus on biodegradable and eco-friendly options. Synthetic fluids with superior cooling and lubrication properties are gaining attention as they reduce waste and health risks associated with traditional cutting fluids.

Selecting and Managing CNC Cutting Fluids for Optimal Performance
CNC cutting fluids are critical in machining, playing key roles in heat dissipation, lubrication, chip removal, and workpiece quality improvement. They also extend tool life, boost productivity, and help manage environmental factors. Understanding the different types of cutting fluids and best practices for maintenance and disposal enables manufacturers to optimize machining performance while minimizing costs and health risks.
As the industry advances, innovations like eco-friendly formulations, AI-driven fluid monitoring, and nano-enhanced lubricants continue to emerge, further improving efficiency and sustainability.
For more information, contact Debaolong Seiko. You are also welcome to upload your designs to Debaolong Seiko for a quote.