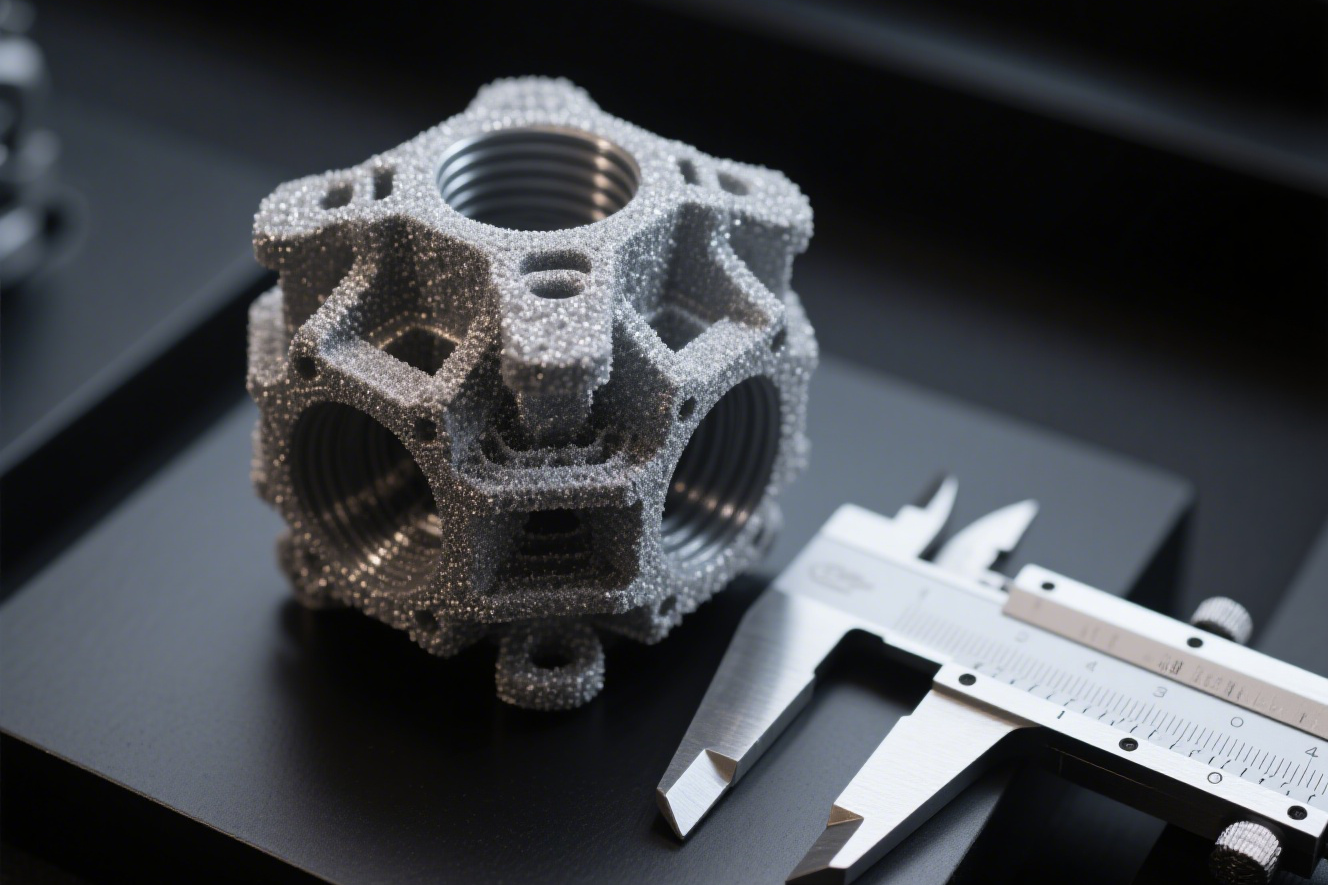
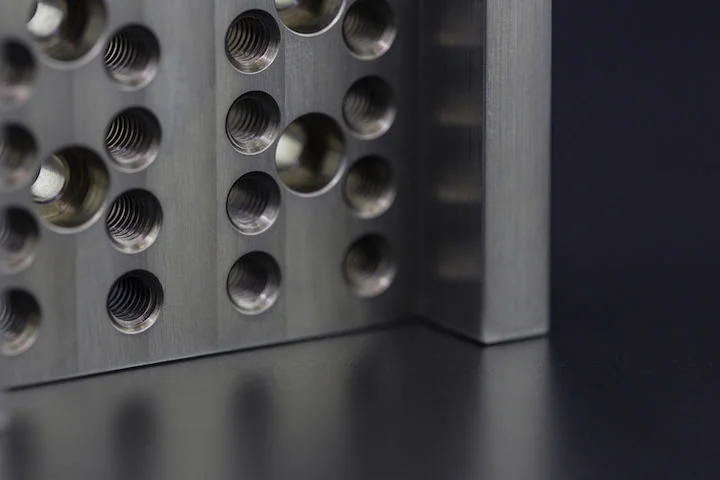
Nowadays, a large number of 3D printers have emerged in the market, and more and more 3D printers are being applied to various fields. For friends who are just getting started with 3D printers, facing the wide variety of 3D printers, they may not know how to choose. Now Debaolong Seiko will briefly introduce the mainstream types of 3D printing technologies.
Principles of 3D Printers
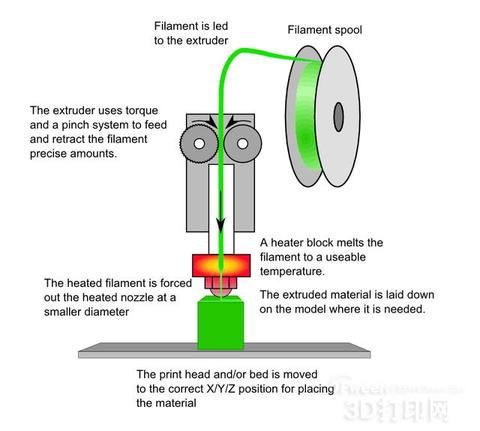
1. FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): Main Materials ABS, PLA, etc.
The FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) process primarily uses thermoplastic materials such as PLA, ABS, and nylon, supplied in filament form. The material is heated and melted in the nozzle. As the nozzle moves along the cross-sectional contour and filling path of the part, the melted material is extruded, rapidly solidifies, and bonds with the surrounding material. Each layer is built upon the previous one, with the upper layer positioning and supporting the current layer.
2. SLA (Stereolithography): Main Material Photosensitive Resin
SLA (Stereolithography) is the earliest rapid prototyping process, based on the photopolymerization principle of liquid photosensitive resin. This liquid material undergoes rapid photopolymerization under ultraviolet light of a specific wavelength and intensity, with a sharp increase in molecular weight, causing the material to transform from liquid to solid. SLA is currently the most researched and technically mature method, with a typical layer thickness of 0.1 to 0.15 mm, enabling high-precision part fabrication.

3. DLP (Digital Light Processing): Main Material Photosensitive Resin
The DLP (Digital Light Processing) technology is similar to SLA, but it uses a high-resolution digital light processor (DLP) projector to cure liquid photopolymers layer by layer. Since each layer is cured as a “slide-like” sheet, it is faster than traditional SLA technology of the same type. This technology offers high molding precision, with material properties, details, and surface finish comparable to injection-molded durable plastic parts.

4. SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): Main Material Powder Materials
The SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) process, also known as selective laser sintering, uses powdered materials for forming. The process involves:
- Spreading a layer of material powder over the surface of the previously formed part and leveling it.
- Scanning the cross-section of the part with a high-intensity CO₂ laser on the newly spread powder layer.
- The powder material is sintered together under the laser’s high intensity, forming the part’s cross-section and bonding with the underlying formed layer.
- After sintering one cross-section, a new layer of powder is spread, and the next cross-section is selectively sintered.